Microfinance Industry – Research Problem, Question and Objectives
Chapter 1 : Microfinance Industry
Introduction :
This Chapter provides a breakdown of the research content.
The reader is to be provided a sense of the task the author is about to highlight in terms of past research work done and gaps, the research problem/question down to the methodology employed and the delimitation faced during the task.
1.1 Project Background
Microfinance institutions in Cameroon are committed to improve the life of the poor or low-income people through the provision of credits, savings and other financial services.
Therefore, they become the core source of funding towards SMEs and the poor.
The Economic and Monetary Community of Central Africa (CEMAC) Regulation does not deal with the legal status of the microfinance industry MFI, but only with its activity.
The above regulation defines Microfinance as an activity made by entities that obtained licences to operate in providing loans, collecting savings, and providing specific financial services to the poor that are not able to access the formal banking service.
Thus, Cameroon’s MFIs are grouped into three categories such as:
- The First Category of MFIs dealing only with their members (cooperatives, associations, and so on);
- The Second Category of MFIs that provide financial services to people. They must act as Limited Companies;
- The Third category of MFIs is those that only provide loans but must not collect savings.
According to a 2006 CEMAC study, there are 714 MFIs in Cameroon, with over 475 thousand clients, making up 2.9 percent of the total population.
The total loans outstanding were reported at USD 111 millions, with the average loan size reported as USD 233.
However, Cameroon’s growing microfinance industry is in need of both regulation and modernization it is to become effective in the fight against poverty.
According to Curtis (2008), key factors for impeding the growth of the microfinance industry might be highlighted as a lack of cooperation between banks and MFIs, as well MFIs are operating with a little use of IT to address the environmental pressures related to modern ways for managing people mostly the poor such as the use of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) which the author aims to point out.
The effectiveness of customer relationship taken as a key to customer value become widely emphasized on improvement with clients for long-term profitability.
However, CRM cannot succeed without the use of IT in a bid to implement relationship management strategies and assisting firms and companies to assemble customer data, identify the most valuable customers, and consequently increase customer loyalty in providing customized products and service.
1.2 Research Problem
Microfinance has received considerable attention in recent years, mostly since Professor Muhammed Yunus and the Grameen Bank were awarded the 2006 Nobel Peace Prize, raising awareness of the role that financial services play in helping poor families manage their precarious lives.
But access to formal financial services is still severely limited in Africa.
According to Jennifer Isern, who leads CGAP’s work in Africa:
“with just one in five households having access to formal financial services, Sub-Saharan Africa suffers from one of the lowest rates of access in the world[…] but there are huge opportunities.
With the right policy direction, Africa is poised for massive expansion in financial services, building on robust economic growth, donor commitment, a strong savings culture, and a very diverse landscape of providers.” (cited in Microcapital, 2008).
The problem to be solved is from the view that the Cameroon microfinance industry is becoming an important tool in reaching out to the majority in low-income stakeholders and thus must involve increase customers-oriented activities.
MFIs seen as amongst the financial services in Cameroon could gain competitive advantage through the use of Customer Relationship Management CRM in their services.
At the moment, these microfinance industry MFI are only focusing on services and products, not considering the customer-factor.
1.3 Research Question
The research problem drives to the following questions:
- How well are the customers segments understood and individually serviced?
- What relevance can CRM tool offer the Management towards value delivery that can gain customer loyalty and satisfaction?
- Can any CRM infrastructure be applicable in Cameroon MFIs which can produce renowned results?
1.4 Project Aims and Objectives
The research is targeted towards the use of CRM through IT within the Cameroon microfinance industry.
The aim of the research is at pointing out a framework of CRM within the Cameroon microfinance industry.
The objectives of the research should be the following:
- To appraise the current level of CRM usage in Cameroon MFIs
- To access how CRM use can deliver an effective customer value
1.5 Significance of Study
The study identifies the important issues, which could be considered by the Cameroon microfinance industry, in order to have technological input to improve marketing aspect within the sector.
The major deliverable from this research is to set a suitable framework to implement Customer Relationship Management CRM in Cameroon MFIs, and this is expected to serve as an eye opener to further research on accessing the extend of the usefulness of technology in the areas of business environment.
1.6 Methodology
Methodology is defined as the philosophy of methods applied by carrying out a research.
This research covers the five fundamental topics that make up an academic research.
Firstly, the author applied the traditional understanding of the research process. The aim and strategies for writing a research project in academic standard is also considered.
The issue of ethical implication of the project is taken in account.
Despite the fact that the concept is publicly overlooked, the author is to adhere to the ethical requirements set by the Institution.
Finally, through data analysis, a statistical-computing software package namely SPSS will be used.
1.7 Outline of the Research
Chapter One includes the project background, the research problems and questions, the aims and objectives, significance of study, and limitations of the research.
In Chapter Two, a critical analysis of the literatures reviewing of the Customer Relationship Management, the current statement of microfinance industry in Cameroon in respect with business environment, mostly the technologies used at present to implement their marketing.
The deliverables will be submitted on the findings and comparison of previous works on this research, and the role of literature review will be essential as the starting point of this report.
The submitted copy will meet the acceptable standard expected of any academic work.
Chapter Three will involve the method of approach to achieving the desired goal of this paper to be embarked upon with respect to the clearly defined research questions, and this is referred to as research methodology.
Then, is the collection of the primary data from the industry as stated and it will entail justification for the choice of research approach.
Chapter Four thereafter will analyze the date and the Five one will in turn involve the formulation of artefact, in solving the research problem. Chapter Six includes drawing-up conclusion after confirming the efficacy of the artefact or the framework/outline; this will be used for answering the research question.
It will also involve recommendations and suggestions made, limitations identified, and self review of entire research.
Figure 1.1 below shows the research design outline.
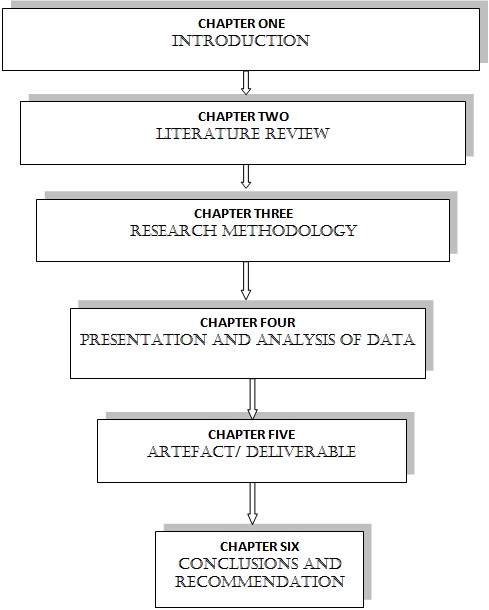
Figure 1.1 Research Design Outline
1.8 Limitations
The focus of the research is the framework of CRM in Cameroon Microfinance industry in perspective to get competitive.
However, the questionnaires were sent out on trust, with the contacts saddle with distributing and collating, there little contacts between the researcher and most of respondents except for the interview personally conducted by the author.
Moreover, the findings were analyzed without the testing of the hypothesis, and the deliverables are theoretical and may require some level of adjustment in real life scenario.
Time constraint was also another factor that limited this project. Since there is a short time frame to complete this research, only necessary areas were analyzed.
Limited resources and publications documents on Customer Relationship Management CRM in Cameroon were as well a blocking factor.
1.9 Conclusion
The microfinance industry is highly resourceful and wide in scope, in terms of its tremendous role it is playing within the new real world.
However, the author focuses the research on the Cameroon Microfinance industry relying on the use of the framework of CRM to enable microfinance industry MFIs to improve in the market place.
Finally, the conclusion of the research is only focussed on the framework or theory-based and consequently will no emphasize on the technical view of the technology.